According to the World Diabetes Day Organization, 463 million adults were living with diabetes in 2019 and this number is expected to rise to 578 million by 2030. Interestingly, it’s been approximately 100 years since Leonard Thompson received the first successful injection of insulin. Excitingly, this day is marked on the 14th of November, the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting who co-discovered insulin along with Charles Best in 1922.
The World Diabetes Day (WDD) was created in 1991 in recognition of the high cases and threats posed by diabetes globally. This year’s theme is Access to Diabetes Care – If Not Now, When? This is in recognition of the fact that many people across the globe are living with diabetes and yet have no access to medical care.
This means that we cannot wait any longer for government and other institutions’ interventions. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes was responsible for at least $760 billion in health expenditure in 2019 – 10% of the global total spent on healthcare.
What is diabetes?
According to the Control for Disease Centre (CDC) diabetes is a chronic and long-lasting health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. If you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin or can’t use the insulin it makes as well as it should.
Diabetes at a glance
- 1 in 2 adults with diabetes remain undiagnosed (232 million). The majority have type 2 diabetes.
- More than 3 in 4 people with diabetes live in low and middle-income countries.
- 1 in 6 live births (20 million) are affected by high blood glucose (hyperglycaemia) in pregnancy.
- Two-thirds of people with diabetes live in urban areas and three-quarters are of working age.
- 1 in 5 people with diabetes (136 million) are above 65 years old.
- Diabetes caused 4.2 million deaths in 2019 (Source World Diabetes Day)
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes
Type 1 diabetes
Also known as insulin-dependent since people who have this type of diabetes need to take insulin every day.

This type of diabetes is an autoimmune disease meaning the body attacks itself where the insulin producing cells in your pancreas are destroyed. Research has shown that 5%-10% of people who have diabetes have type 1. It is mostly diagnosed among children and young adults.
- Type 2 diabetes
- According to Cleveland Clinic, this type of diabetes occurs when your body doesn’t make enough insulin or the body cells don’t respond normally to insulin. It is the most common type of diabetes with up to 95% of the people with diabetes having this type 2. It is prevalent among middle-aged and older people.
- Gestational diabetes
- This type of diabetes is common in women during pregnancy. This type develops in some women during their pregnancy. It is hyperglycaemia with blood glucose values above normal but below those diagnostics of diabetes.
DIABETES IN KENYA
- In Kenyan adults, the nationally adjusted prevalence of diabetes was estimated to be 3.6% in 2013 and is projected to rise to 4.4% by 2035, this is according to The National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- In Kenya, diabetes prevalence is higher in urban populations and men.
- It is estimated that as many as 60% of people with diabetes in Kenya remain undiagnosed
Symptoms
Diabetes symptoms vary depending on how much your blood sugar is elevated
Mayo Clinic says that some people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, may sometimes not experience symptoms. In type 1 diabetes, symptoms tend to come on quickly and be more severe.
Some of the signs and symptoms of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes are:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Extreme hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores
- Frequent infections, such as gums or skin infections and vaginal infections
Risk factors
Risk factors for diabetes depend on the type of diabetes.
Risk factors for Type 1
- Having a family history of type 1 diabetes.
- Injury to the pancreas
- Presence of autoantibodies that mistakenly attack your body’s tissues or organs
- Physical stress such as surgery or illness
- Exposure to illnesses caused by viruses
Risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or Type 2 diabetes
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American, Asian-American race, or Pacific Islander.
- Being overweight.
- Having high blood pressure.
- Having low HDL cholesterol
- Being physically inactive
- Being age 45 or older
- Having gestational diabetes or giving birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds.
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Having a history of heart disease or stroke.
- Being a smoker.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include:
- Family history of prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
- Being African-American, Hispanic, Native American or Asian-American.
- Being overweight before your pregnancy.
- Being over 25 years of age
Can diabetes be cured?
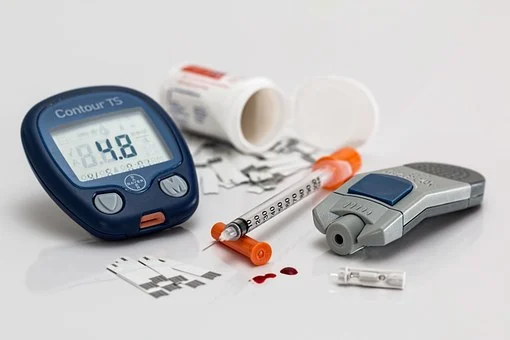
According to Medical News Today, diabetes is not curable, however, a person can stay in remission for a long time. This means that When diabetes goes into remission, it means that the body does not show any signs of diabetes, although the disease is technically still present.
As we celebrate this day, WHO is using the 100th anniversary of the discovery of insulin to highlight the huge gap between the people who need access to insulin to control their diabetes, as well as essential technologies such as blood glucose meters and test strips and those who have access.
MYDAWA has ensured that some of the medical devices necessary for managing the disease are available. They include testing strips, blood sugar and pressure monitors. All these items can be purchased on the MYDAWA platform and delivered the same day. With the Corona virus pandemic, we have recorded a huge number of people living with diabetes being hospitalized with COVID-19. It is therefore an opportunity for us to leverage on this day to raise awareness on the need to educate citizens about the disease.
0




